The flu (influenza) is an infection of the nose, throat, and lungs that is caused by the influenza virus. Based on the recent number of influenza cases in Malaysia, it seems like the flu season is upon us now. No new strains, just mainly Influenza A making its presence known.1
Common symptoms of influenza:
When influenza strikes, it can leave you feeling absolutely miserable. Influenza tends to come on rapidly with symptoms like:
High fever and chills
Runny or stuffy nose
Body/muscle aches and headaches
Extreme fatigue and weakness
Dry, persistent cough
Sore throat
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (more common in children)
Most cases of influenza can be managed from home, but it’s important to know when to seek professional medical care. Persistent or severe cases should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out complications.
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in this equation!
While it can’t replace medical treatment, optimal nutrients can help to blow the flu away.
When it comes to building and sustaining a well-rounded immune defense, nutrients are essential in working together to rebuild and repair cells, support natural defenses, and optimize our body’s response to infections.
Here’s a closer look at powerful immune-support nutrients:
Vitamin C
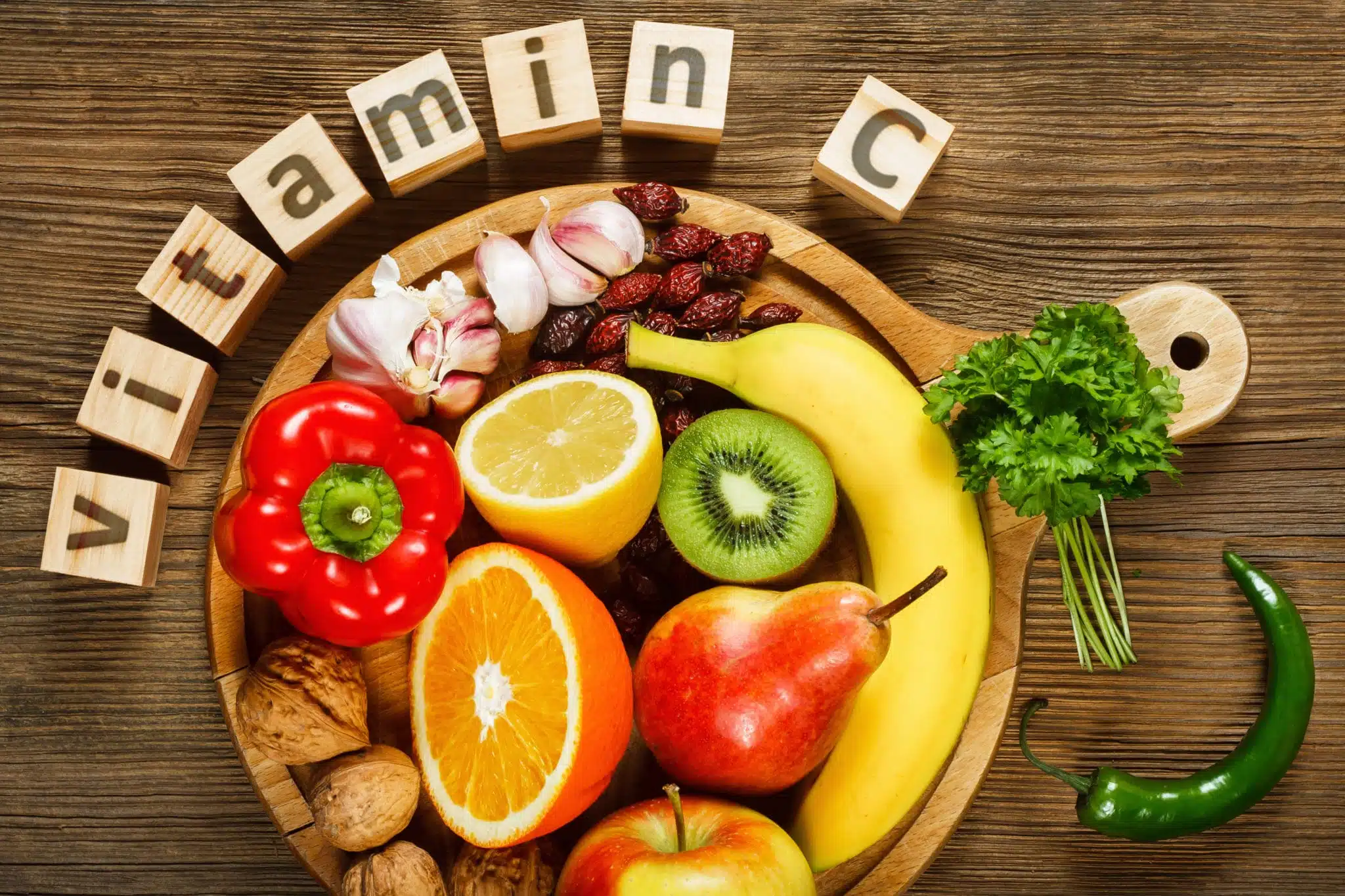

Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant that helps your immune cells work more effectively to detect and fight germs. A lack of Vitamin C can make you more prone to colds and respiratory infections. While it may not completely prevent colds, getting enough Vitamin C can help reduce how long and how severe they are.2,3
Since your body cannot store Vitamin C, it’s important to get it regularly from foods like citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, bell peppers and broccoli.
Vitamin A
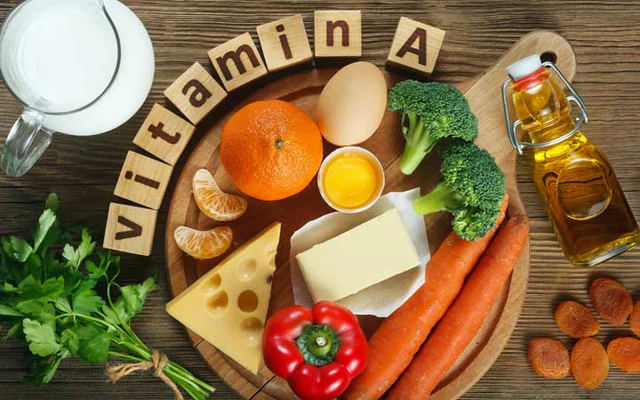

In addition to its well-known role in eye health, Vitamin A helps strengthen immune defences, making it easier to stay healthy and recover faster when you’re sick.4,5
Vitamin A-rich foods like liver, eggs, dairy, and orange-colored vegetables can support immune function.
Vitamin D
Since its discovery, vitamin D or often called the "sunshine vitamin," has been known for its implications in maintaining bone health. It has been discovered that Vitamin D also modulates the immune response and reduces respiratory infection risk. Low vitamin D levels are linked to a higher risk of infections and weaker protection from the flu.6,7
Because vitamin D deficiency is common, it’s important to get enough through sunlight, fortified foods or supplements to keep your defenses strong.
Zinc
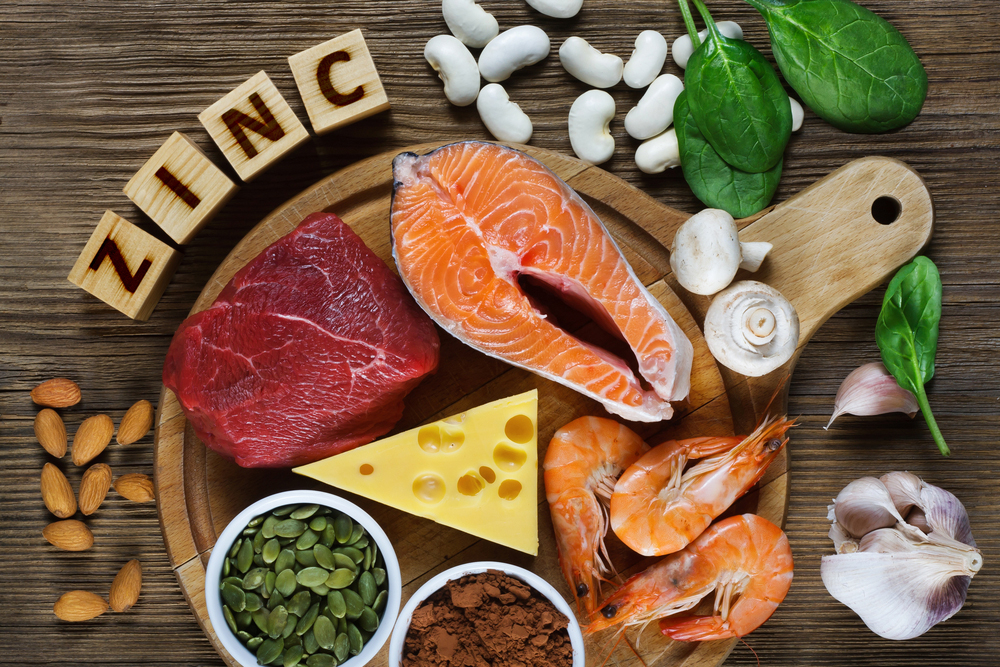

Zinc helps your immune cells detect and fight infections while keeping inflammation under control. Its antioxidant effect helps protect immune cells from damage and keeps them working efficiently. Low zinc levels are linked to a higher risk of infections and weaker responses to vaccines.8,9
Foods rich in zinc include meat, shellfish, legumes, seeds and whole grains.
Selenium

This antioxidant mineral supports the body’s response to viral infections. It plays an important role in antiviral defense and helps prevent viruses from mutating and becoming stronger. Studies show that low selenium levels can weaken the body’s defenses, making infections more severe and, making viruses like influenza harder to control.10
Selenium-rich foods include Brazil nuts, seafood, eggs and whole grains.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their benefits to heart and brain health, but they’re equally important for immune health. Omega-3s, particularly EPA and DHA, are essential in moderating inflammation.
Studies have shown that omega-3s, especially those from Fish Oil, can help to reduce excessive inflammation and maintain optimal immune function by modulating immune cell activity and reducing the production of inflammatory molecules.11
Probiotics

A healthy gut helps keep the immune system strong, as most immune cells live in the digestive tract. Probiotics support this by keeping the gut balanced and helping the body fight off harmful germs.12
Yoghurt and other traditional fermented foods, such as sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh, kefir and the increasingly popular drink kombucha are rich sources of probiotic to help maintain a balanced gut microbiome.
Try these natural essentials to boost recovery and get back on your feet!
While the flu is never fun, many cases can be managed from the comfort of home with some self-care and patience. Here are some essentials to be consider:
Honey
Honey, in general, and particularly manuka honey supports flu recovery with nutrients and compounds like methylglyoxal (MGO), antioxidants, vitamins and minerals that provide antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.13 These help soothe sore throats, calm coughs and aid the body’s natural healing process.
Tea


Tea can be considered natural essentials to help boost recovery from influenza. Not as cures, but as supportive remedies that help the body heal faster and feel better. Especially ginger tea contains active compounds like gingerol and shogaol, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties14, while green tea is rich in catechins, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), known for its strong antioxidant and antiviral effects.15
Sauerkraut

As mentioned earlier, probiotics are live good bacteria that help keep your gut healthy and support overall immune balance. Sauerkraut is one of the fermented foods rich in beneficial bacteria (probiotics) that can support recovery from influenza.16Lemon

Lemon is rich in vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that supports immune cell function and helps the body fight infections more effectively. Yes, 100% lemon juice can be considered a natural essential to help boost recovery from influenza.
Moringa

Moringa, often called the “drumstick tree” or “miracle tree,” is a nutrient-rich plant native to South Asia and parts of Africa. The leaves are especially valued because they’re packed with nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin A, zinc, iron, and antioxidants, all of which play important roles in strengthening the immune system and helping the body fight infections.
Supplements
If it’s hard to meet your needs through diet alone, taking a suitable supplement can be a convenient way to support your immune health.
Note: These are not substitutes for medical treatment, especially if you have flu or complications. Always consult a healthcare professional.
Reference:
New Straits Times. (2025, October 21). Virologist urges public to mask up as influenza cases rise. New Straits Times. https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2025/10/1298864/virologist-urges-public-mask-influenza-cases-rise
Holford, P., Carr, A. C., Jovic, T. H., Ali, S. R., Whitaker, I. S., Marik, P. E., & Smith, A. D. (2020). Vitamin C-An Adjunctive Therapy for Respiratory Infection, Sepsis and COVID-19. Nutrients, 12(12), 3760. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123760
Hemilä, H., & Chalker, E. (2023). Vitamin C reduces the severity of common colds: A meta-analysis. BMC Public Health, 23, 2468. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-17229-8
Gürbüz, M., & Aktaç, Ş. (2022). Understanding the role of vitamin A and its precursors in the immune system. Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme, 36(2), 89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nupar.2021.10.002
Huang, Z., Liu, Y., Qi, G., Brand, D., & Zheng, S. G. (2018). Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System. Journal of clinical medicine, 7(9), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090258
Galindo-Méndez, M., Galindo-Ruiz, M., Concheso-Venegas, M. F., Mendoza-Molina, S. U., Orozco-Cruz, D., & Weintraub-Benzion, E. (2025). The Impact of Vitamin D in the Prevention of Influenza, COVID-19, and Dengue: A Review. Biomedicines, 13(4), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13040927
Zhu, Z., Zhu, X., Gu, L., Zhan, Y., Chen, L., & Li, X. (2022). Association Between Vitamin D and Influenza: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Frontiers in nutrition, 8, 799709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.799709
Sadeghsoltani, F., Mohammadzadeh, I., Safari, M. M., Hassanpour, P., Izadpanah, M., Qujeq, D., Moein, S., & Vaghari-Tabari, M. (2022). Zinc and Respiratory Viral Infections: Important Trace Element in Anti-viral Response and Immune Regulation. Biological trace element research, 200(6), 2556–2571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02859-z
Gopal, R., Tutuncuoglu, E., Bakalov, V., Wasserloos, K., Li, H., Lemley, D., DeVito, L. J., Constantinesco, N. J., Reed, D. S., McHugh, K. J., Chinnappan, B., Andreas, A. R., Maloy, A., Bain, D., Alcorn, J. F., Pitt, B. R., & Kaynar, A. M. (2024). Zinc deficiency enhances sensitivity to influenza A associated bacterial pneumonia in mice. Physiological Reports, 12(1), e15902. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.15902
Sadler, R. A., Mallard, B. A., Shandilya, U. K., Hachemi, M. A., & Karrow, N. A. (2024). The Immunomodulatory Effects of Selenium: A Journey from the Environment to the Human Immune System. Nutrients, 16(19), 3324. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193324
Poggioli, R., Hirani, K., Jogani, V. G., & Ricordi, C. (2023). Modulation of inflammation and immunity by omega-3 fatty acids: A possible role for prevention and to halt disease progression in autoimmune, viral, and age-related disorders. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 27(13), 7380–7400.
Wang, Y.-H., Limaye, A., Liu, J.-R., & Wu, T.-N. (2023). Potential probiotics for regulation of the gut-lung axis to prevent or alleviate influenza in vulnerable populations. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 13(2), 161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.08.004
Watanabe, K., Rahmasari, R., Matsunaga, A., Haruyama, T., & Kobayashi, N. (2014). Anti-influenza viral effects of honey in vitro: potent high activity of manuka honey. Archives of medical research, 45(5), 359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.05.006
Ayustaningwarno, F., Anjani, G., Ayu, A. M., & Fogliano, V. (2024). A critical review of Ginger's (Zingiber officinale) antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities. Frontiers in nutrition, 11, 1364836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1364836
Rawangkan, A., Kengkla, K., Kanchanasurakit, S., Duangjai, A., & Saokaew, S. (2021). Anti-Influenza with Green Tea Catechins: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 26(13), 4014. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134014
Muhialdin, B. J., Zawawi, N., Abdull Razis, A. F., Bakar, J., & Zarei, M. (2021). Antiviral activity of fermented foods and their probiotics bacteria towards respiratory and alimentary tracts viruses. Food control, 127, 108140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108140